Prerequisites: This article assumes familiarity with forex trading and MetaTrader 4 platform.
When discussing forex trading, most people's immediate perception is that it involves high risk and high returns, making it seemingly inaccessible to the average investor. Let's examine this perception in detail.
Let's first address the source of risk. Many immediately point to high leverage as the primary risk factor. While forex trading typically involves leverage ratios of hundreds to one, and sometimes even thousands to one, is leverage truly the root cause of risk? Consider the Chinese stock market over the past 30 years - despite minimal use of leverage, it has demonstrated significant risk. This counterexample suggests that the relationship between leverage and risk may not be as straightforward as commonly believed. Let's analyze a real trading case study to understand the true sources of risk and potential risk management strategies.
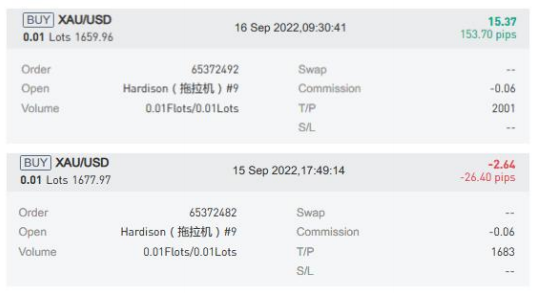
In the above chart, the first position shows a gold purchase at $1,659.96 per ounce for 0.01 lots, currently showing a floating profit of $15.37. The second position, opened at $1,677.97 for 0.01 lots, shows a floating loss of $2.64. Note that these floating profits and losses are independent of the leverage ratio or margin requirements.
From a theoretical perspective, minimizing margin requirements - or maximizing leverage - is optimal, as account capital should primarily serve as a risk buffer rather than being tied up in position margins. Indeed, some forex brokers now offer infinite leverage, meaning positions require no margin - a reflection of advanced credit economics.
Given this understanding, why does the perception persist that high leverage equals high risk? The answer lies in trading behavior. Consider a scenario with infinite leverage: while it's technically possible to open 100 lots of gold positions with just a $100 account, any minor adverse price movement would generate floating losses far exceeding the account balance, leading to immediate margin call. The only scenario where this might work is if the market immediately moves in your favor - an extremely risky gamble. This misuse of leverage creates the illusion that leverage itself is the primary risk factor.
This analysis clearly demonstrates that risk stems from trading behavior rather than leverage itself. This understanding provides a solid theoretical foundation for our risk management approach: consistently trading with minimal position sizes (0.01 lots) to effectively control position risk.
Regarding returns, it's crucial to first understand the four main components of forex trading costs: spreads, commission, overnight holding costs (swap), and slippage. Spreads are generally transparent and vary by account type - ECN accounts typically offer the tightest spreads, followed by STP accounts, while cent accounts have wider spreads. Trading commissions are usually only applicable to ECN accounts.
Overnight holding costs (swap rates) are often overlooked by traders despite their significance. These rates vary considerably between brokers and can differ for long versus short positions. Some brokers offer swap-free Islamic accounts. Let's examine a real trading example to illustrate this impact.
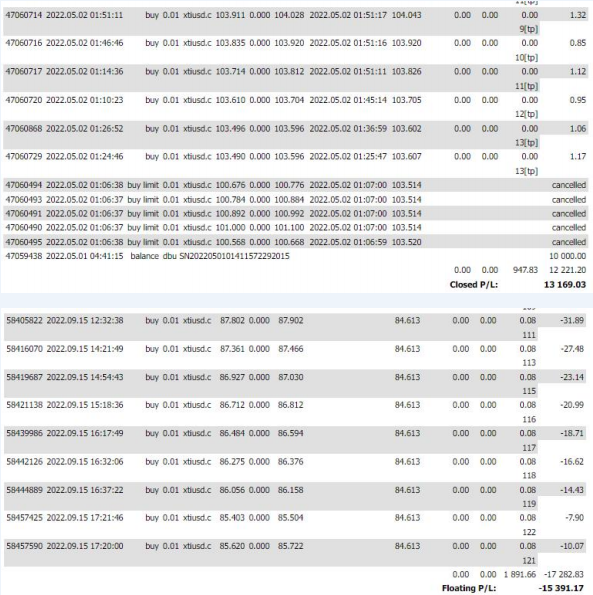
The charts above show our live crude oil trading account. The accumulated swap fees total $2,839.49 ($947.83 from closed positions and $1,891.66 from open positions). Relative to the initial capital of $10,000, this represents a 28.39% return from swap fees alone over 4.5 months (May 1 to September 16), equivalent to an annualized return exceeding 70% - a remarkable contribution to overall performance.
Finally, there's slippage - price differences between expected and actual execution levels. This typically occurs during market opens or periods of high volatility, affecting both entry and exit orders. Slippage represents an unquantifiable and uncontrollable risk that can only be properly assessed through actual trading experience with a specific broker. While some less reputable brokers may manipulate slippage to their advantage, it's worth noting that slippage can also work in traders' favor. The extent of slippage depends not only on the broker's MT4 server infrastructure but also on the design of the trader's EA (Expert Advisor) systems. Let's examine a real-world example.
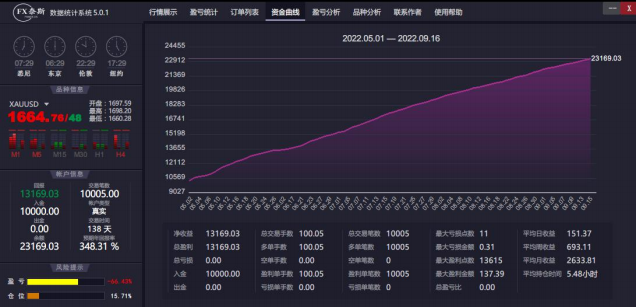
The chart above displays our live crude oil trading account performance. The total closed profit stands at $13,169.03, or $12,221.20 after deducting swap fees of $947.83. Our EA was configured to target a profit of 1 point per trade across 10,005 transactions, theoretically yielding 10,005 points in total profit. However, the actual realized profit of $12,221.20 exceeds this target by $2,216.20 - a surplus attributable to positive slippage. This represents a 22.16% return from slippage alone over 4.5 months, equivalent to an annualized return exceeding 50% - a significant performance enhancement.
In conclusion, we propose an innovative approach to forex education, particularly emphasizing the value of cent accounts for early learning. We advocate introducing forex trading to young individuals from age 10, regardless of gender, using 10,000-cent demo accounts. This early exposure, combined with proper discipline and risk management training, even through multiple account iterations if necessary, can develop into professional-level trading competency by age 18. This approach leverages the enhanced learning plasticity of youth, contrasting with the often costly learning curve experienced by adults who may lose substantial capital due to ingrained trading behaviors and cognitive biases. This educational approach represents not just trading instruction, but the development of a valuable life skill in financial markets.
Through systematic analysis of risk sources, development of mitigation strategies, and comprehensive understanding of trading costs, forex trading becomes a more approachable endeavor. By focusing on high-probability setups and maintaining disciplined risk management, traders can navigate the forex market more effectively. We invite readers to consider this analytical approach to forex trading.
